UNITED STATES DEPARTMENT OF ENERGY
Executive Summary: Overview
The U.S. Department of Energy’s (DOE’s) Wind and Water Power Technologies Office led a comprehensive analysis to evaluate future pathways for the wind industry. Through a broad-based collaborative effort, the Wind Vision had four principal objectives:
- Documentation of the current state of wind power in the United States and identification of key technological accomplishments and societal benefits over the decade leading up to 2014;
- Exploration of the potential pathways for wind power to contribute to the future electricity needs of the nation, including objectives such as reduced carbon emissions, improved air quality, and reduced water use;
- Quantification of costs, benefits, and other impacts associated with continued deployment and growth of U.S. wind power; and
- Identification of actions and future achievements that could support continued growth in the use and application of wind-generated electricity.
The conclusions of this collaborative effort, summarized below, demonstrate the important role that wind power has in the U.S. power sector and highlight its potential to continue to provide clean, reliable and affordable electricity to consumers for decades to come. The Wind Vision study does not evaluate nor recommend policy actions, but analyzes feasibility, costs, and benefits of increased wind power deployment to inform policy decisions at the federal, state, tribal, and local levels.
A High U.S. Wind Penetration Future is Achievable, Affordable and Beneficial
Wind power is one of the fastest-growing sources of new electricity capacity and the largest source of new renewable power generation added in the United States since 2000. Changes in wind power market dynamics, costs, technology, and deployment since the 2008 DOE report, 20% Wind Energy by 2030, are documented through analysis of recent history, current status (as of 2013), and projected trends. The analysis of wind installation and operational experience as of 2013 concludes that:
- Wind deployment, including associated manufacturing and installation activities, has demonstrated the ability to scale to satisfy rapid build demands, including the deployment levels of the Wind Vision Study Scenario described below;
- Wind generation variability has a minimal and manageable impact on grid reliability and related costs; and
- Environmental and competing use challenges for local communities, including land use, wildlife concerns, and radar interference issues, can be effectively managed with appropriate planning, technology, and communication among stakeholders.
Deployment of wind technology for U.S. electricity generation provides a domestic, sustainable, and essentially zero-carbon, zero-pollution and zero-water use U.S. electricity resource.
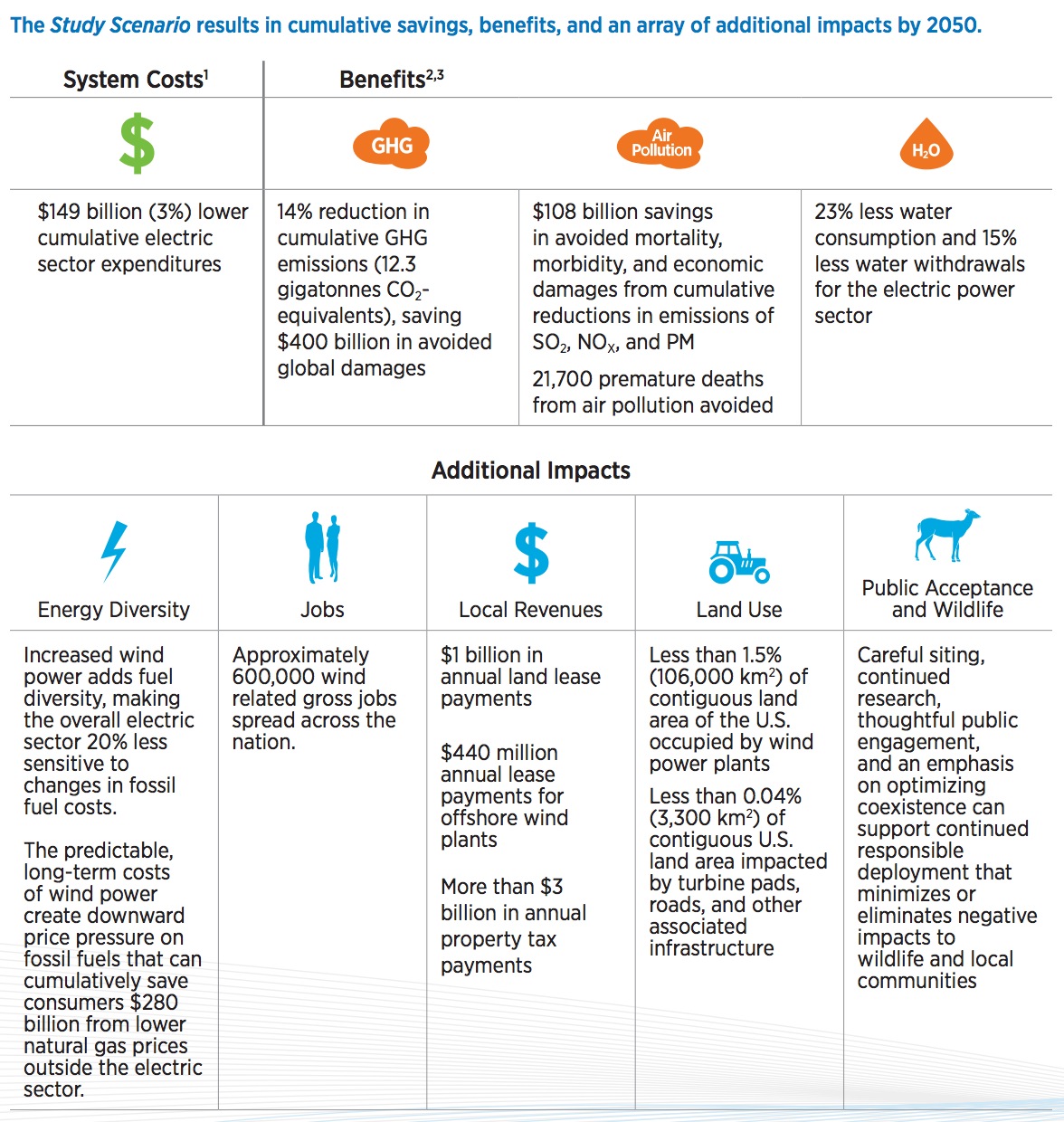
The Wind Vision report deepens the understanding of U.S. wind power’s potential contributions to clean, reliable electricity generation and related economic and other societal benefits. Results are provided from analyses of U.S. greenhouse gas (GHG) and pollution reductions, electricity price impacts, job and manufacturing trends, and water and land use impacts—for the years 2020, 2030, and 2050. A high U.S. wind penetration is achievable but will require actions as identified in the Wind Vision Roadmap.
Study Summary
The Wind Vision report results from a collaboration of the DOE with over 250 experts from industry, electric power system operators, environmental stewardship organizations, state and federal governmental agencies, research institutions and laboratories, and siting and permitting stakeholder groups. The Wind Vision report updates and expands upon the DOE’s 2008 report, 20% Wind Energy by 2030, through analysis of scenarios of wind power supplying 10% of national end-use electricity demand by 2020, 20% by 2030, and 35% by 2050. This Study Scenario provides a framework for conducting detailed quantitative impact analyses. The Wind Vision analysis concludes that it is both viable and economically compelling to deploy U.S. wind power generation in a portfolio of domestic, low-carbon, low-pollutant power generation solutions at the Study Scenario levels. Realizing these levels of deployment, however, would depend upon both immediate and long-term actions—principally identifying continued wind cost reductions, adding needed transmission capacity, and supporting and enhancing siting and permitting activities—to complement any federal, state, tribal, and local policies that may be enacted. Described in the Wind Vision Roadmap, these actions focus on specific key challenges and stakeholder actions that should be considered.
Download full version (PDF): A New Era for Wind Power in the United States
About the United States Department of Energy
Energy.gov
The mission of the Energy Department is to ensure America’s security and prosperity by addressing its energy, environmental and nuclear challenges through transformative science and technology solutions.
Tags: U.S. DOE, United States Department of Energy, Wind Energy






 RSS Feed
RSS Feed