OFFICE OF THE VICE PRESIDENT OF THE UNITED STATES
EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
With over $787 billion in funding, the American Recovery and Reinvestment Act is one of the single boldest and largest investments in the U.S. economy in the nation’s history. The Recovery Act’s design was three-fold: to rescue a rapidly deteriorating economy; put the country on a path to recovery by putting Americans back to work quickly; and reinvest in the country’s long-term economic future, building a foundation for a new, more robust, and competitive American economy.
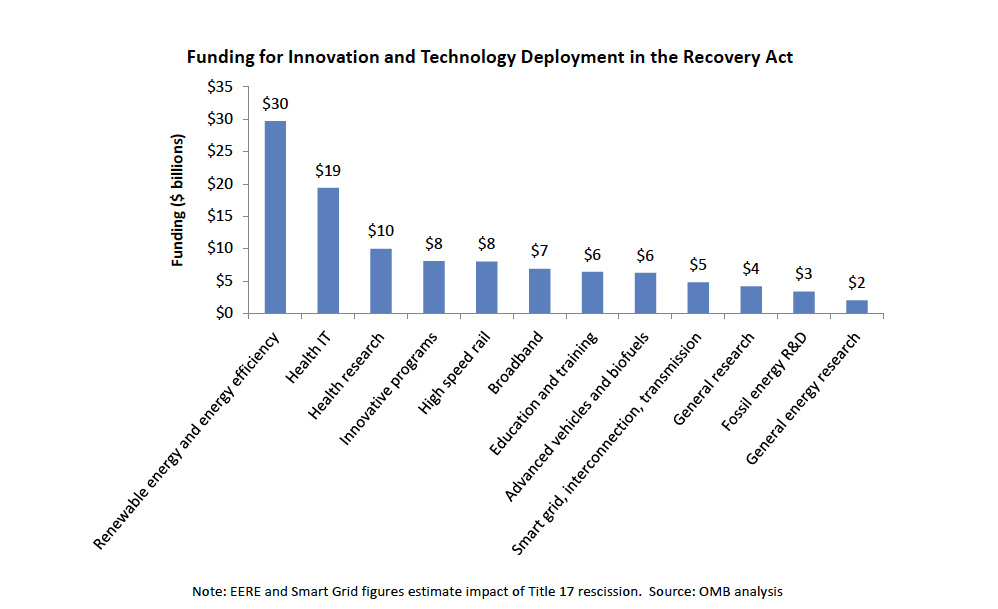
Within the reinvestment spending of the Recovery Act, over $100 billion is invested in innovative and transformative programs. This report explores four areas within those innovative programs in which game-changing breakthroughs are being sought, and in some cases, new American industries are being born:
1. Modernizing transportation, including advanced vehicle technology and high-speed rail;
2. Jumpstarting the renewable energy sector through wind and solar energy;
3. Building a platform for private sector innovation through investments in broadband, Smart Grid, and health information technology; and
4. Investing in groundbreaking medical research.
Modernizing Transportation, including Advanced Vehicle Technology and High-Speed Rail
In 2009, the U.S. had only two factories manufacturing advanced vehicle batteries that power electric vehicles and produced less than two percent of the world’s advanced vehicle batteries. The Recovery Act is investing over $2 billion in advanced battery and electric drive component manufacturing. By 2012, 30 factories with the capacity to produce an estimated 20 percent of the world’s advanced vehicle batteries will exist in the U.S. At full scale, they will produce enough batteries and components to support 500,000 plug-in and hybrid electric vehicles.
Between 2009 and 2013, when 20 Recovery-Act funded battery factories will be up and running, battery costs are expected to drop by half – cutting an electric car’s cost premium in half. Looking further into the future, Recovery Act-funded start-ups like Envia and FastCAP are pursuing technologies that could take us well beyond today’s best lithium-ion batteries. This will create lighter, cheaper, and more powerful electrical energy storage devices such as batteries, allowing for better mileage, greater safety, and better acceleration—putting the U.S. in position to build the best cars in the world.
Outside the Recovery Act, the Advanced Technology Vehicles Manufacturing program is providing over $2.4 billion in loans to Fisker, Nissan, and Tesla to support three of the world’s first electric car factories in Delaware, Tennessee, and California, respectively. These investments will increase U.S. manufacturing capability in the near future.
The future of transportation in the U.S. will also benefit from better rail travel. With $8 billion in funds, the Recovery Act is beginning to make high-speed rail a reality across the country. For example, the California high-speed rail mega-project promises to alter significantly the transportation landscape in the state by connecting its largest metropolises with up to 220-mph service.
Jumpstarting the Renewable Energy Sector through Wind and Solar Energy
The Recovery Act is helping to deploy more rapidly the latest generation of solar power technologies while expanding manufacturing of these technologies here in the U.S. The Section 1603 Payments-In-Lieu-Of-Tax-Credits program is supporting more than 200 megawatts (MW) of solar projects that are already delivering solar power to consumers. In Pensacola, Florida, the program has helped fund the 25 MW DeSoto Solar Park, the largest photovoltaic power plant in North America that consists of over 90,000 solar panels. The Section 48C Advanced Energy Manufacturing Tax Credits are helping solar manufacturers like FirstSolar, which is expanding a large manufacturing plant in Perrysburg, Ohio. Loan guarantees are helping innovative thin-film solar manufacturer Solyndra build a high-tech solar module manufacturing facility in Fremont, California, with the capacity to produce modules totaling 230 MW each year. In addition, the U.S. Department of Energy has issued a conditional commitment for a loan guarantee to support the 400 MW BrightSource solar thermal project, the world’s largest solar thermal facility with approximately 349,000 mirrors.
In addition, the Recovery Act is helping to ramp up production of wind energy and its component manufacturing base in the U.S., maintaining strong demand and financing for projects and helping attract billions of dollars of additional private investment. The Section 1603 program has provided over $3 billion in payments-in-lieu-of-tax-credits to more than 100 wind projects in 30 states around the country, totaling 5.3 GW of wind power capacity. The Section 48C Manufacturing Tax Credit program awarded $346 million in tax credits for 52 wind manufacturing projects across the country, which will substantially increase U.S. wind manufacturing capacity to meet a growing market with domestic production.
The Recovery Act is supporting breakthrough innovations in both solar and wind. FloDesign in Massachusetts is developing a novel shrouded wind turbine design with advanced aerospace technology that should reduce the cost and noise of wind energy dramatically. Likewise, companies like 1366 Technologies and Semprius are developing new approaches to make solar cells much less expensive than today’s best thin film technology.
Building a Platform for Private Sector Innovation through Investments in Broadband, Smart Grid, and Health Information Technology
A stronger economy must also rely on smarter energy use, a more efficient health administration system, and more robust and wide-reaching information transmission network. Significant investments in broadband aim to bring America’s telecommunications capacity into the 21st century, increasing access, improving quality, and driving down the cost to access broadband for millions of Americans. In addition to the $4.4 billion provided to the Department of Commerce, $2.5 billion in funds was provided to the Department of Agriculture to increase broadband access in rural America. Millions of Americans, as well as tens of thousands of anchor institutions will have better access to broadband as a result. Farmers will be able to access real-time weather reports, water conditions, and crop commodity pricing, helping them be as competitive as possible in a global market.
To further empower consumers in their energy usage decisions, increase flexibility, and enhance reliability, a combination of Recovery Act funds and private investments will add 18 million new smart meters to the eight million currently in use. To improve system reliability, the Recovery Act will install more than 875 transmission system sensors that can alert system operators and help prevent minor disturbances from cascading into large outages. Finally, for further system reliability, the Recovery Act funds will help equip approximately 700 substations with automated devices to detect and respond to system irregularities, thereby helping to avoid outages.
The Recovery Act is investing approximately $20 billion in health information technology to boost significantly advancements in electronic health records, e-prescribing, e-care, and community health initiatives. Through the $250 million Beacon Communities program, communities will demonstrate the use of new technologies aimed at sustainable improvements in health outcomes, health care quality, safety, and efficiency. These efforts will not only cut certain medical costs, but also improve care. Finally, the rise in e-care technologies or telemedicine will allow medical personnel to treat patients remotely, while being able to monitor conditions and prescribe or administer medications from miles away.
…
Download full report (PDF): The Recovery Act
Tags: ARRA, Barack Obama, Executive Office, HSR, Joe Biden, President of the United States, Recovery Act, Renewable Energy, Solar Energy, Vice President, White House, Wind Energy






 RSS Feed
RSS Feed