DEPARTMENT OF APPLIED ECOLOGY
NORTH CAROLINA STATE UNIVERSITY
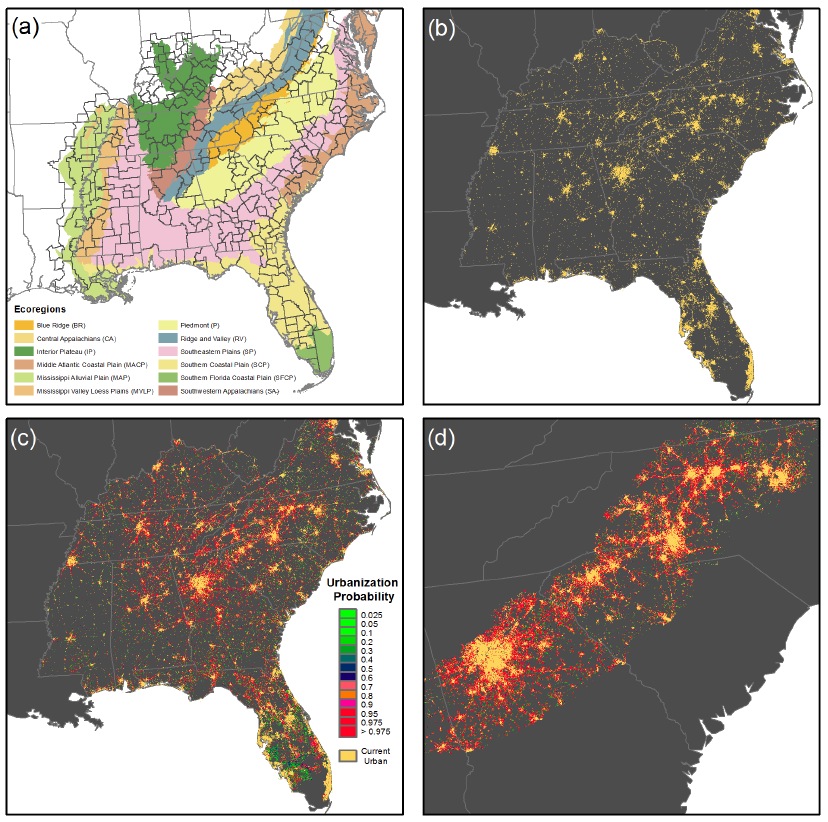
Cities are expanding, and as they do urban sprawl–low-density urban development outside the urban core–is expanding even more rapidly. In some regions, expansion of suburban habitats as a result of shifts to automobile-dependent living has led to increases in the urban footprint even where populations have not shown large increases. Urban sprawl increases the connectivity among urban habitats while simultaneously fragmenting non-urban habitats such as forests and grasslands. These changes have a variety of effects on species and ecosystems, including impacts to water pollution, disturbance dynamics, local climate, and predator-prey relationships. Urban sprawl will also, almost certainly, influence the ability of species to respond to climate change, in as much as it creates barriers to the movement of species that cannot survive in cities and corridors for those who can. Knowledge about the potential future character of urban sprawl is thus useful to a variety of stakeholders, including resource managers, conservation organizations, and urban planners.













 RSS Feed
RSS Feed