AMERICAN COUNCIL ON RENEWABLE ENERGY
Executive Summary
The Midwest’s remarkable renewable energy resources, vast agricultural land, strong manufacturing base, and leading research institutions have propelled the region to become a hub for renewable energy development. It is home to over a third of U.S. wind power capacity and 80% of U.S. biofuel production capacity. However, uncertainty about federal policy – like the production tax credit (PTC) and renewable fuels standard (RFS) – as well as transmission constraints could hinder Midwestern renewable energy capacity additions in the near term, with 2013 expected to yield only a fraction of the installations seen in previous years. Nevertheless, increasingly affordable project costs and state renewable energy targets will continue to drive market momentum in the region, as indicated by recent, positive signals given by renewable energy companies and utilities.
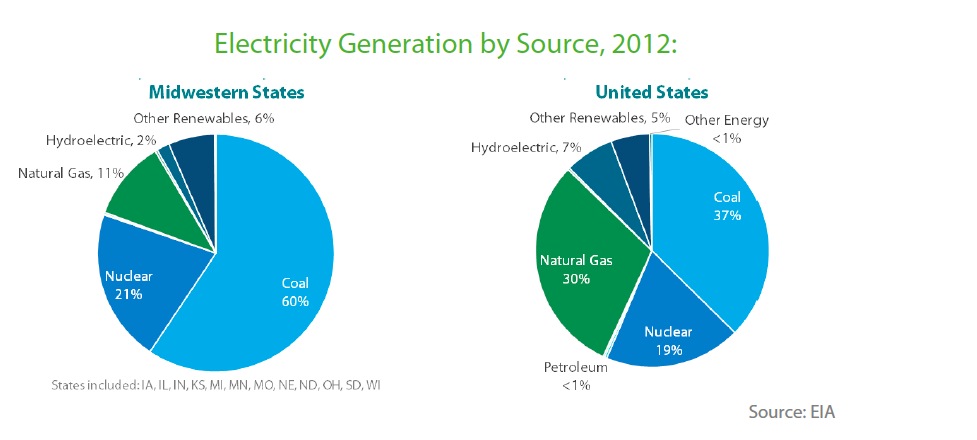
While coal dominates the Midwest’s power supply, the states recognize the importance of renewable energy and have set targets for its use and deployment. Out of the 12 states profiled in this report, eight have binding standards for renewable and/or clean energy and three have non-binding goals. A number of the states support these targets through an array of financial incentives for wind power, on-farm energy, biofuels, solar power, and other renewable energy systems.
The cost of building renewable energy projects continues to decline in many Midwestern states, facilitated by the region’s nationally recognized wind and bioenergy resources. As a result, two of Michigan’s largest utilities recently eliminated a surcharge on their customers’ bills originally designed to cover the cost of meeting the state’s renewable portfolio standard, indicating that renewable energy projects are costing them less than expected. In addition, a major investor-owned utility recently chose wind power as its technology of choice because of its “lower costs than other possible resources,” in its announcement to build four new power projects in the Midwest. These four projects would add 600 MW of wind energy capacity to the grid and power up to 750,000 homes.
Home to the Corn Belt and much of the nation’s agricultural activity, nine of the top ten biofuel states by production capacity are located in the Midwest. Companies and universities spearhead advanced biofuel research in Midwestern states, with numerous pilot and small-scale facilities that develop cellulosic and algae-sourced fuels, and development is underway on the first facilities that will produce advanced biofuels at commercial scale. Airlines and the U.S. military also see the region as a proving ground for aviation fuels. Major airlines work with biofuel companies and research institutions to grow feedstocks for and produce renewable jet fuel in the Midwest, with plans to launch biofuel-powered planes from Midwestern airports. In May 2013, the U.S. Department of Defense chose Nebraska to be the location of a biofuel plant that will sustainably power jets and ships by 2016. Nevertheless, the continued growth of and investment in renewable fuels in the Midwest is in question if the federal RFS is scaled back or repealed.
Over a third of U.S. wind capacity is located in the Midwest. Five Midwestern states generate over 10% of their electricity from wind energy, out of only nine states nationally. Last year resulted in a 29% increase in installed generation capacity in the Midwest, adding over 21 GW of new wind power to the grid. However, uncertainty caused by Congressional debate over the PTC, coupled with transmission constraints, have resulted in far fewer wind power facilities to be built to date in 2013.
Wind power and biofuels are far from the only renewable technologies used in the Midwest:
- Solar power saw a 150% boost in capacity in 2012, with 200 MW now connected to the grid in Midwestern states. Policies that encourage distributed generation, like net metering, also spur the growth of residential and commercial solar energy markets in states such as Wisconsin and Missouri.
- Many states use their considerable agricultural and other biomass resources, like corn stover, to produce bioenergy. The Midwest’s numerous dairy farms, wastewater treatment plants, and other facilities produce biogas for electricity, heat, and fuel, helping to reduce air and water pollution.
- Waste-to-energy projects in several states convert municipal solid waste into electricity and/or steam for use as an energy source for municipalities and private industry.
- Renewable heating technologies, like biomass thermal, geothermal heat pumps, and solar thermal, can be used to offset the region’s reliance on imported fossil fuels for heating purposes.6 Waste heat to power technologies capture heat from industrial processes to produce electricity, and are considered renewable in at least six Midwestern states.
- Hydropower is an important energy resource in some Midwestern states, responsible for 49% of electricity generation in South Dakota.
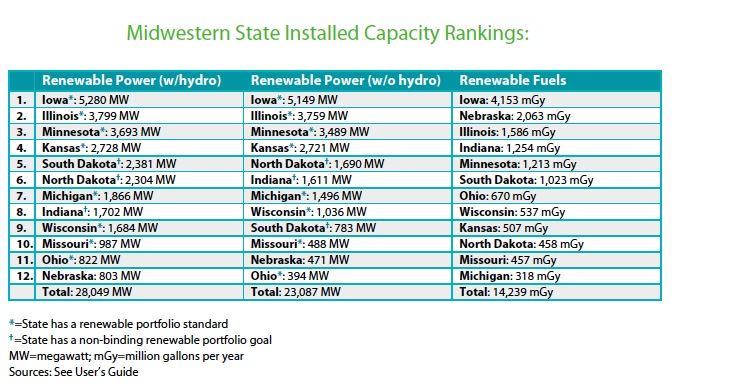
Despite the industry’s recent growth, electricity transmission inadequacies stifle large-scale development so that many states tap into only a fraction of their available resources.8 New transmission line proposals in Illinois, Iowa, Michigan, Missouri, Nebraska, and North Dakota could help to open bottlenecks and encourage continued renewable energy development.
The importance of renewable energy in the Midwest will continue to grow as it becomes an increasingly competitive alternative to fossil fuel generation.
Download full report (PDF): Renewable Energy in the 50 States – Midwest
About the American Council on Renewable Energy
www.acore.org
ACORE, a 501(c)(3) non-profit membership organization, is dedicated to building a secure and prosperous America with clean, renewable energy. ACORE provides a common educational platform for a wide range of interests in the renewable energy community, focusing on technology, finance and policy. We convene thought leadership forums and create energy industry partnerships to communicate the economic, security and environmental benefits of renewable energy.
Tags: ACORE, American Council on Renewable Energy, Biofuel, Midwest, Solar, Wind Energy






 RSS Feed
RSS Feed