LINCOLN INSTITUTE OF LAND POLICY
Executive Summary
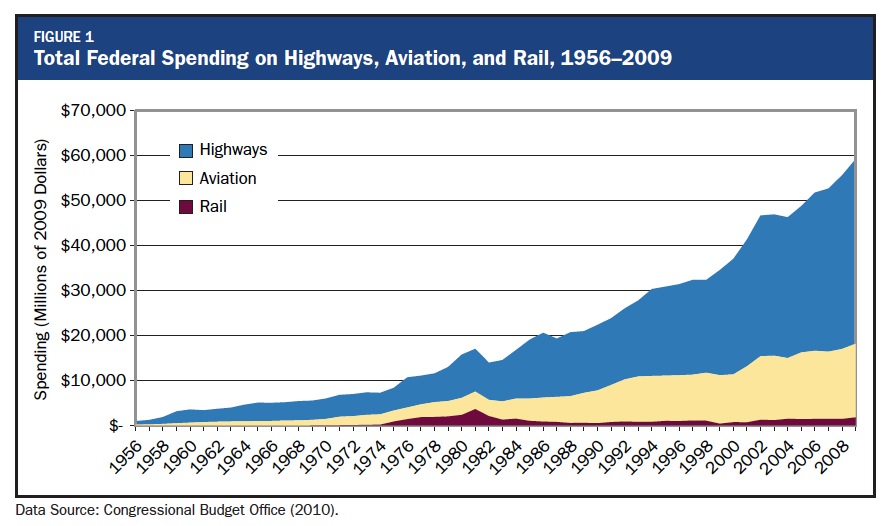
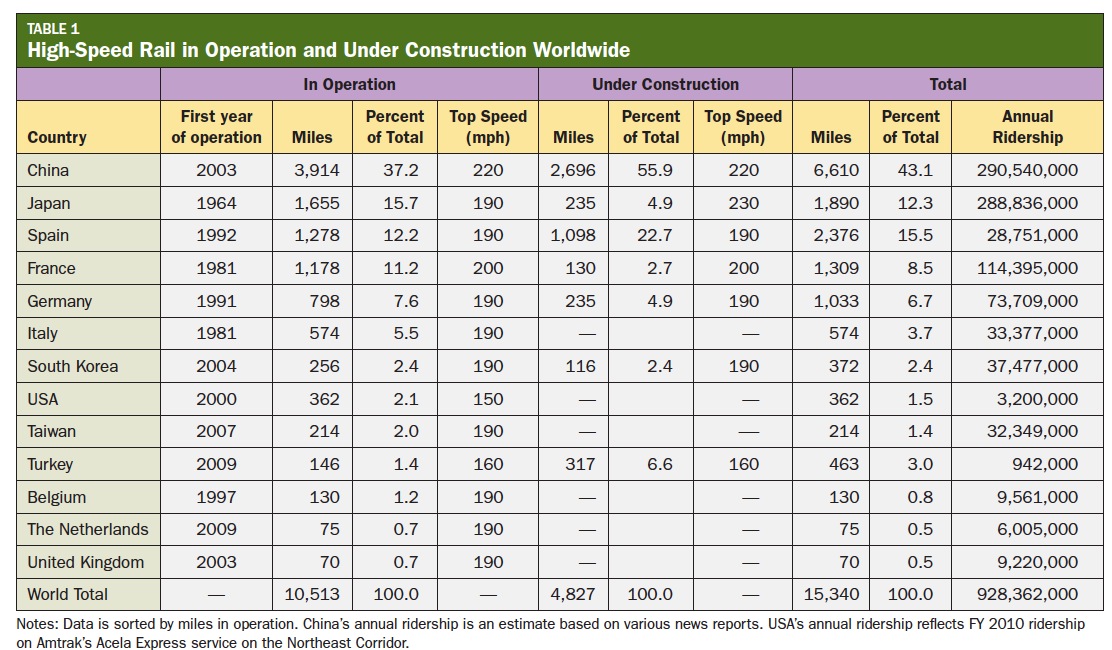
High-speed rail has been adopted throughout the world, and is now being planned and developed in the United States. Over the past 50 years, U.S. transportation spending has favored the development of interstate highway and aviation systems. In the meantime, countries such as China, Japan, Spain, France, and Germany have been investing in modern high-speed rail systems to satisfy the travel demands of current and future generations. As the United States embarks on the High-Speed Intercity Passenger Rail Program launched in 2009, it can learn from the experiences of other countries i planning, constructing, and operating high-speed rail.
In 2009–2010, the U.S. Congress appropriated $10.1 billion for a new high-speed and intercity passenger rail program. Applications from 39 states requested nearly $75 billion, demonstrating broad interest in and support for this program. The available funds were awarded to dozens of conventional intercity passenger rail projects and a few dedicated high-speed rail projects in 32 states and the District of Columbia, and those projects are now moving forward.
The U.S. Department of Transportation, which manages the passenger rail program, has adopted a tiered approach, which emphasizes investments appropriate to the different markets and geographies in the United States. It defines three categories of passenger rail service that are intended to work together as a network: Core Express refers to high-speed trains operating on dedicated tracks with frequent service; Regional service operates at moderately high speeds and high frequency on shared corridors; and Emerging/ Feeder service is less frequent and connects smaller and emerging markets to major markets located along Regional and Core Express routes.
Decades of international experience with high-speed rail suggests that it could create similar transportation, economic, environmental, and safety benefits in American cities and regions. While it requires high upfront investment, high-speed rail promotes economic growth by improving market access, boosting productivity of knowledge workers, expanding labor markets, and attracting visitor spending. When planned thoughtfully with complementary investments in the public realm, high-speed rail can promote urban regeneration and attract commercial development, as shown in several European examples. High-speed rail has greater operating energy efficiency than competing modes and takes up less land than highways.
The initial investment of $10.1 billion in the U.S. High-Speed Intercity Passenger Rail Program, after years of minimal federal investment, required that the federal government and participating states quickly scale up to the challenge of laying the groundwork for a foundational program and implementing it at the same time. Those states that had the staff capacity, expertise, and experience in rail planning, such as Illinois, North Carolina, and Washington, were successful in securing high-speed rail grants. However, carrying the momentum of this initial investment forward has proven to be a struggle in a difficult fiscal environment, and California is currently the only federally funded Core Express high-speed rail project moving forward. In 2011, Congress voted to strip funding from the program. The expiration of the legislation authorizing the high-speed rail program in 2013 may provide an opportunity to consider policy changes.
Download full version (PDF): High-Speed Rail: International Lessons for U.S. Policy Makers
About the Lincoln Institute of Land Policy
www.lincolninst.edu
“The Lincoln Institute of Land Policy is a leading resource for key issues concerning the use, regulation, and taxation of land. Providing high-quality education and research, the Institute strives to improve public dialogue and decisions about land policy. As a private operating foundation whose origins date to 1946, the Institute seeks to inform decision making through education, research, policy evaluation, demonstration projects, and the dissemination of information, policy analysis, and data through our publications, Web site, and other media. By bringing together scholars, practitioners, public officials, policy makers, journalists, and involved citizens, the Lincoln Institute integrates theory and practice and provides a nonpartisan forum for multidisciplinary perspectives on public policy concerning land, both in the U.S. and internationally.”
Tags: Daniel Schned, Lincoln Institute of Land Policy, Petra Todorovich, Robert Lane






 RSS Feed
RSS Feed