GOVERNMENT ACCOUNTABILITY OFFICE
Introduction
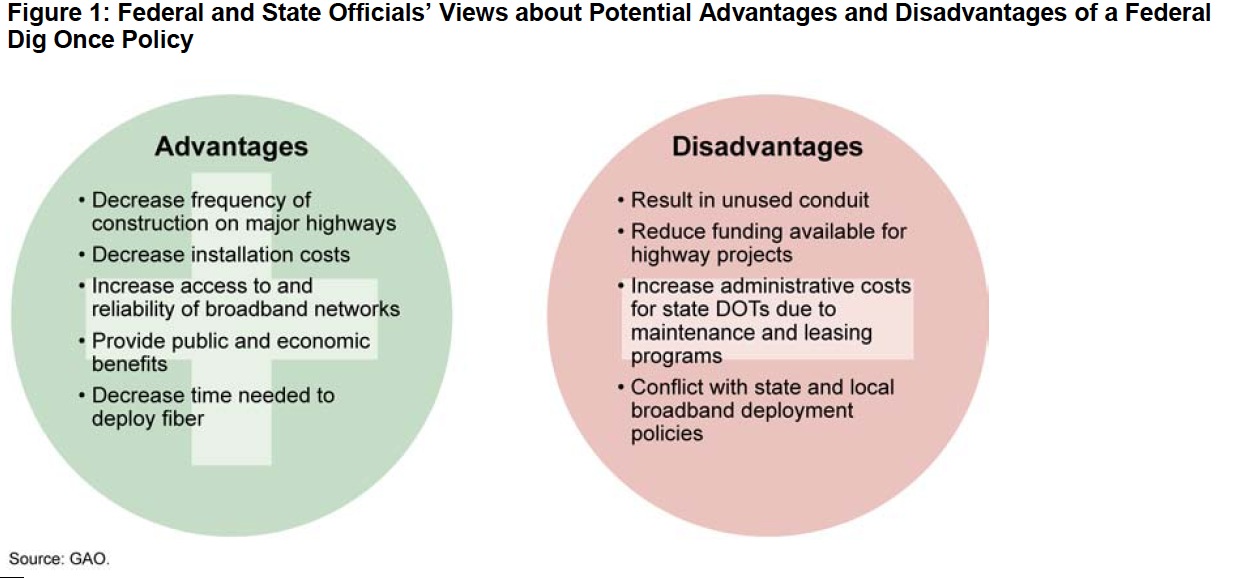
Affordable access to broadband telecommunications is increasingly viewed as vital to the country’s economic growth as well as for improving state and local systems for traffic management, public safety, and educational goals. According to the Federal Communications Commission (FCC), the largest cost element for deploying broadband via fiber optic cable is the cost of placement, such as burying the fiber in the ground, rather than the cost of the fiber itself. Recent legislation introduced in both the U.S. Senate and House of Representatives would require the Secretary of Transportation to require states to install broadband conduit during construction for certain federally funded highway projects in compliance with standards developed by the Secretary, in coordination with FCC. Both the House and Senate bills would make conduit available to any requesting broadband service provider for a “charge not to exceed a cost-based rate.” Both bills would affect only new construction or highway expansion projects that receive federal funding and would not, for example, affect projects limited to road resurfacing or general maintenance.
About the GAO
www.gao.gov
“The U.S. Government Accountability Office (GAO) is an independent, nonpartisan agency that works for Congress. Often called the “congressional watchdog,” GAO investigates how the federal government spends taxpayer dollars. The head of GAO, the Comptroller General of the United States, is appointed to a 15-year term by the President from a slate of candidates Congress proposes. Gene L. Dodaro became the eighth Comptroller General of the United States and head of the U.S. Government Accountability Office (GAO) on December 22, 2010, when he was confirmed by the United States Senate. He was nominated by President Obama in September of 2010 and had been serving as Acting Comptroller General since March of 2008.”






 RSS Feed
RSS Feed