THE PEW CHARITABLE TRUSTS
Energy Storage for the Evolving Power System
Overview
Distributed energy resources allow electricity to be generated closer to where it is used, protecting businesses and institutions from unexpected outages caused by natural disasters and other disruptions. The U.S. national laboratories as well as public-private partnerships provide financial resources and access to research facilities to foster innovations to modernize the power sector from a 100-year-old centralized system to one that incorporates disparate clean technologies such as microgrids, batteries, and energy smart tools. These investments and the resulting new products and capabilities decrease costs, improve grid reliability, reduce emissions, and offer consumers more options.
Energy storage technologies encourage adoption of renewable energy by addressing generation variation resulting from weather conditions. They also aid local utilities by providing an array of grid-balancing services, such as peak shifting—shifting grid usage by consumers from periods of high demand to less intensive times—and backup power supplies. These characteristics support a cleaner and more reliable electric system and present an important market opportunity for the clean energy economy.
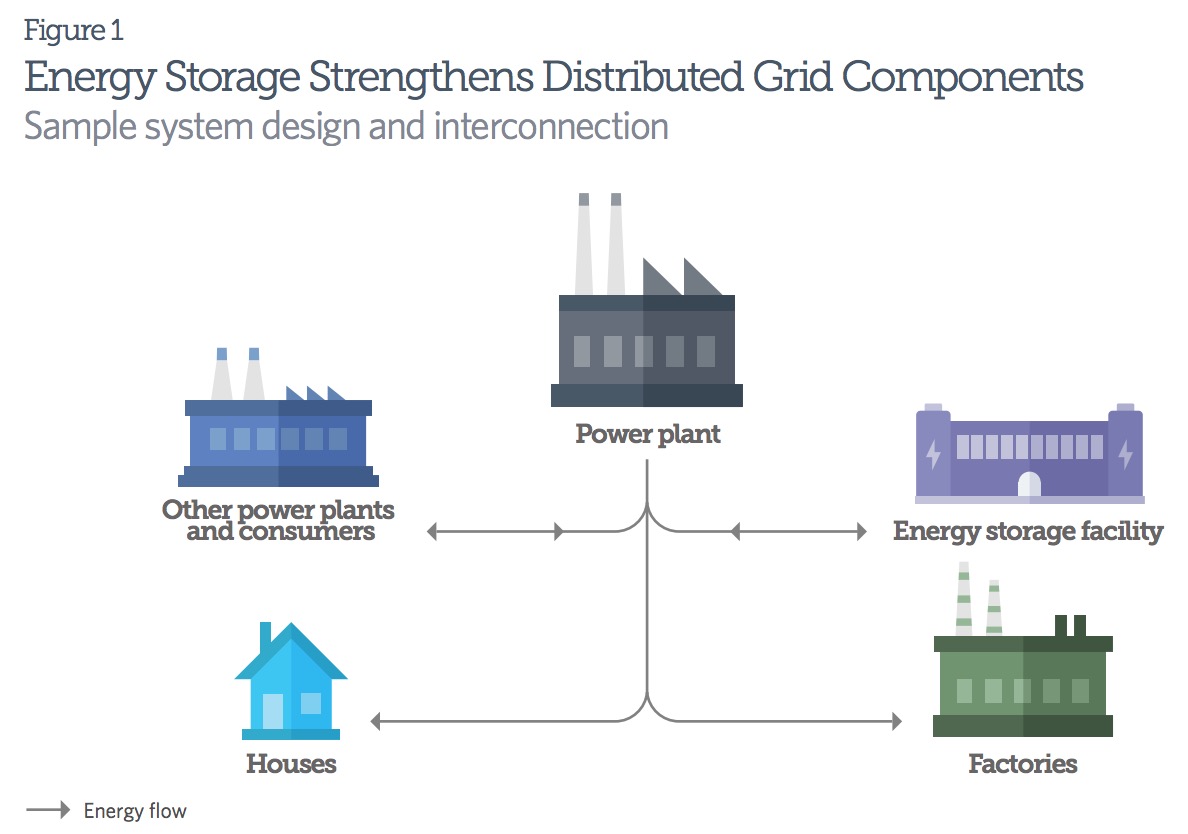
Energy storage makes the system more efficient
Although demand for electricity often varies by the minute, changing the nation’s generating capacity is a slow process. Energy storage technologies enable utilities to better match fixed capacity with variable demand and offer more reliable, secure, and affordable service.
Batteries are an emerging storage option that can improve the central grid’s reliability and increase the use of clean and efficient power sources. For example, when the wind is blowing but demand is low, batteries capture energy from spinning wind turbines and save it for later use. Energy storage can similarly enhance the usability of solar and other intermittent renewable resources. Batteries also offer environmental benefits because they have no emissions.1 Further, energy storage supports local utilities by enabling peak shifting, providing backup power and ancillary grid services,2 and potentially reducing the need for additional fossil-fueled generation sources.
Energy Storage Technologies
A variety of innovative technologies are capable of capturing energy as it is produced and storing it until it is needed. Among the leading approaches are:
- Batteries. These devices convert stored chemical energy into electrical energy. A variety of types are available, including lithium-ion, sodium sulfur, and lead acid, and more chemical alternatives are being developed.
- Flywheels. This mechanical device converts electricity into kinetic energy by constantly spinning a small rotor. When needed, energy is released back to the grid through a turbine-like device.
- Electrochemical capacitors. These systems store electrical charge in solid materials rather than converting charges to another form through chemical or phase changes, as occurs in batteries.
- Superconducting magnetic energy storage. These units employ superconducting coils, power conditioning systems, and cooling mechanisms to inductively store energy
About the Pew Charitable Trusts
www.pewtrusts.org
From its first day in 1948, Pew’s founders steeped the new institution with the entrepreneurial and optimistic spirit that characterized their lives. As the country and the world have evolved, we have remained dedicated to our founders’ emphasis on innovation. Today, Pew is a global research and public policy organization, still operated as a non-partisan, non-governmental organization dedicated to serving the public.
Tags: Distributed Generation, Energy Storage, Pew Charitable Trusts, Pew Trusts






 RSS Feed
RSS Feed