BROOKINGS INSTITUTE
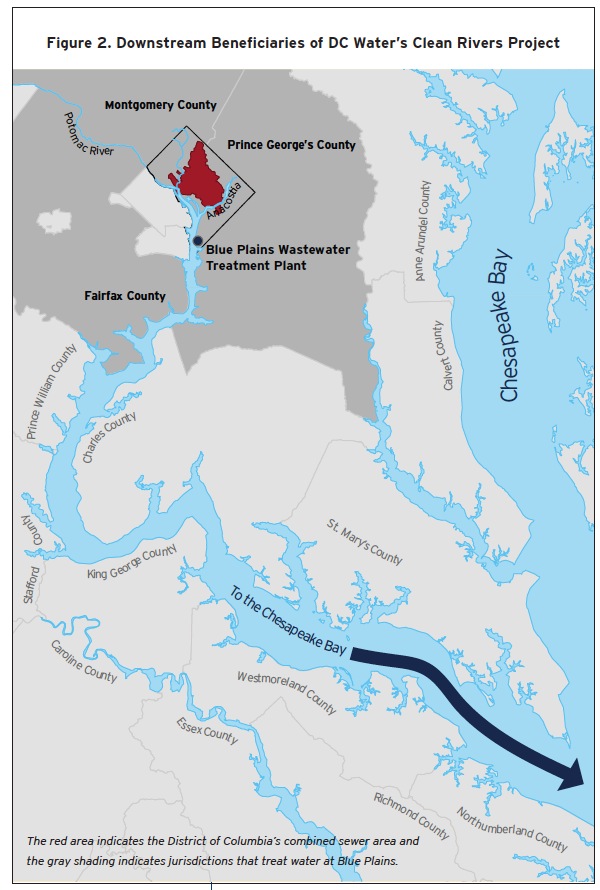
The nation’s capital, like other older American cities, is partially served by a combined sewer system (CSS) in which pipes carry both storm water and sewage or waste water. In dry weather, waste water flows to the Blue Plains Advanced Wastewater Treatment Plant at the southern tip of the District along the Potomac River. After heavy rains, however, the capacity of the combined sewer is often exceeded, and a mixture of sewage an storm water—combined sewer overflows (CSOs)—discharges into the Anacostia and Potomac rivers and Rock Creek, leading ultimately to downstream destinations, including the Chesapeake Bay.















 RSS Feed
RSS Feed