PEDESTRIAN AND BICYCLE INFORMATION CENTER
Executive Summary
1.1 PURPOSE AND BACKGROUND OF THE GUIDE
With the introduction of new and more advanced bike sharing programs, and the continued interest and political support for them throughout many U.S. cities, it is important to provide an objective analysis of bike share programs, and to document early lessons learned. This guide is intended to serve as a resource for transportation planning professionals, as well as public officials considering implementation of a bike sharing program. The guide presents a snapshot of current municipal bike share systems where local jurisdictions (including cities, counties, etc.) are engaged in the funding, managing, administering and/or permitting of bike share implementing practices.
The objectives of this guide are to:
- Define bike sharing and provide an overview of the concept.
- Describe the steps a jurisdiction should take to plan, implement, and sustain a bike share program.
- Document existing models of provision, infrastructure considerations, and funding options for successfully implementing a bike sharing program.
- Describe metrics for monitoring and evaluating program success.
- Provide a baseline documentation of existing bike share programs in the United States in 2012.
1.2 WHAT IS BIKE SHARING?
Bike sharing is an innovative transportation program, ideal for short distance point-to-point trips providing users the ability to pick up a bicycle at any self-serve bike station and return it to any bike station located within the system’s service area.
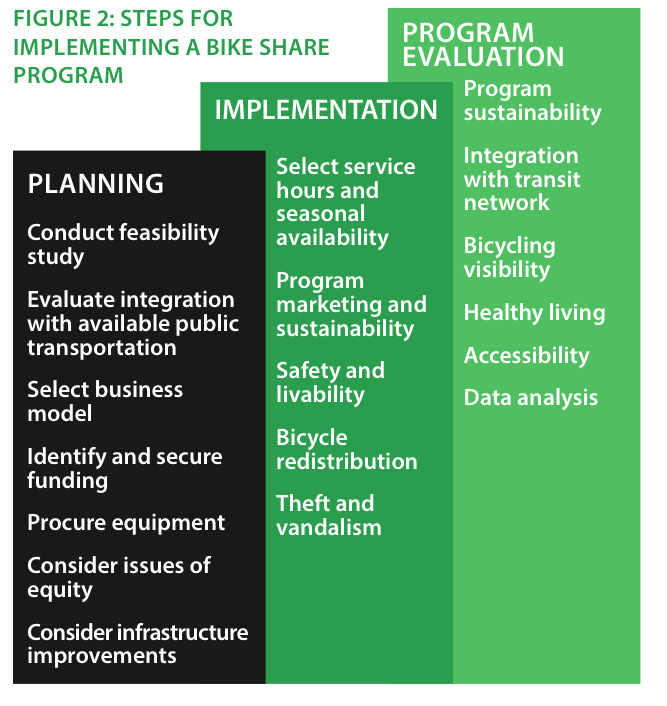
While still very young, modern American bike share programs build on lessons learned from their European and Canadian counter parts, with some differences in technology and operations. In the context of this study, bike sharing differs from traditional bicycle rental services in that it is typically used for short distance and duration trips that are often combined with public transit. Figure 2 delineates the steps jurisdictions should take for implementing a bike share program.
With increasing political and financial support for bike share programs in many major U.S cities, it has become important to document the early lessons learned by pioneering programs, and to provide an initial set of best practices for the next generation of bike share programs. Interest in bike share has been fueled by success in several cities, including Washington, DC, Denver and Minneapolis, where bike share has quickly become an accepted and popular transportation option. It will be important to track the progress of bike sharing implementation as new and more advanced programs are implemented in the next few years.
This guide has been organized in four sections to match with the program development process: Planning, Implementation, Program Evaluation and Additional Considerations. The following is a summary of the findings and recommendations in each of these areas.
About the Pedestrian and Bicycle Information Center
www.pedbikeinfo.org
“Our mission is to improve the quality of life in communities through the increase of safe walking and bicycling as a viable means of transportation and physical activity. Through our comprehensive Web sites, we offer information and training to diverse audiences about health and safety, engineering, advocacy, education, enforcement, access, and mobility as it relates to pedestrians and bicyclists.”
Tags: pedbikeinfo.org, Pedestrian and Bicycle Information Center






 RSS Feed
RSS Feed